what is a Copper Core PCB?
A Copper Core PCB, also known as a Copper Core Printed Circuit Board or Copper Substrate PCB, is a type of printed circuit board designed with a central core layer made primarily of copper. Unlike traditional PCBs where the core is typically made of non-conductive materials like FR-4 (a type of epoxy-based glass-reinforced laminate), a Copper Core PCB has a core that is primarily composed of copper, which provides excellent thermal conductivity.

The primary application of Copper Core PCBs is in electronic devices and systems that generate a significant amount of heat, such as high-power LEDs, power amplifiers, and various automotive components. The high thermal conductivity of copper helps dissipate heat efficiently, preventing overheating and ensuring the reliable operation of these components.
Copper Core PCBs are typically constructed with multiple layers, including copper layers, dielectric layers (to isolate the copper traces and provide electrical insulation), and often a thin layer of thermally conductive material on the top surface to enhance heat dissipation. These boards are used in situations where maintaining a lower operating temperature is critical for the longevity and performance of electronic components.
In summary, a Copper Core PCB is a specialized type of printed circuit board with a central core layer primarily made of copper, designed to facilitate efficient heat dissipation in electronic devices prone to generating significant heat during operation.
Difficulties in Copper Core PCB design and production
Designing and producing Copper Core PCBs presents several challenges compared to conventional FR-4 PCBs due to their unique characteristics and requirements. Some of the difficulties in Copper Core PCB design and production include:
- Thermal Management: The primary reason for using Copper Core PCBs is their superior thermal conductivity. However, effectively managing and distributing heat throughout the board can be challenging. Designers must consider the placement of components, vias, and thermal pads to ensure even heat dissipation.
- Material Selection: Selecting the right core material is crucial for Copper Core PCBs. Different copper core materials have varying thermal conductivity properties, and choosing the wrong material can lead to inadequate heat dissipation or mechanical stability issues.
- Dielectric Thickness: The dielectric layers between the copper core and outer layers must have precise thicknesses to maintain electrical isolation while allowing efficient heat transfer. Achieving the correct dielectric thickness can be challenging, and variations can impact performance.
- Layer Alignment: Copper Core PCBs often have multiple layers with different materials and thicknesses. Ensuring proper alignment during fabrication is essential to prevent warping, delamination, or electrical shorts.
- Cost: Copper Core PCBs tend to be more expensive than traditional PCBs due to the cost of copper and specialized materials. The additional production steps required for thermal management can also contribute to higher costs.
- Machining and Drilling: Machining copper is more challenging than working with FR-4. Specialized equipment and tooling are often required to create precision holes and cutouts in the copper core, adding complexity to the manufacturing process.
- Electrical Isolation: Maintaining electrical isolation between copper traces and components on the top and bottom layers can be challenging, especially when dealing with high-power designs. Careful design and insulation materials are necessary to prevent electrical shorts.
- Handling and Assembly: Copper Core PCBs are heavier and more rigid than standard PCBs, which can make them more difficult to handle during assembly. Specialized assembly techniques and equipment may be required.
- Testing and Quality Control: Ensuring the reliability and performance of Copper Core PCBs requires rigorous testing and quality control measures, including thermal cycling, electrical testing, and inspection for defects.
- Supplier Expertise: Finding a reliable PCB manufacturer with expertise in Copper Core PCB fabrication is essential. Not all PCB manufacturers have the capability to produce these specialized boards to high-quality standards.
Despite these challenges, Copper Core PCBs are essential for applications where efficient heat dissipation is critical. Overcoming these difficulties requires a combination of careful design, material selection, and collaboration with experienced PCB manufacturers to ensure the desired performance and reliability of the final product.
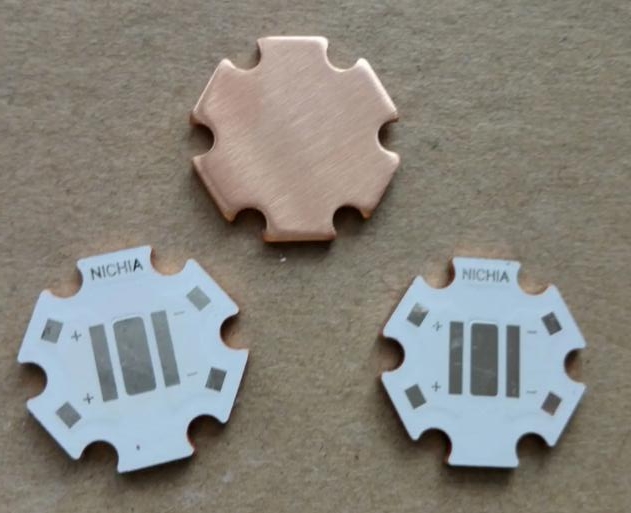

The similarities and differences between copper core PCB and aluminum core PCB
Copper Core PCBs and Aluminum Core PCBs are both specialized types of printed circuit boards designed for applications where efficient heat dissipation is crucial. They share some similarities but also have key differences, particularly in their core materials. Here’s a comparison of the two:
Similarities:
1. Thermal Management: Both Copper Core PCBs and Aluminum Core PCBs are used primarily for their superior thermal conductivity properties. They are designed to dissipate heat generated by components more effectively than traditional FR-4 PCBs.
2. Applications: Both types of PCBs are commonly used in high-power electronics and LED applications, as well as in devices where temperature control is critical to maintain performance and reliability.
3. Layered Structure: Both PCB types typically have multiple layers, including a core material with high thermal conductivity sandwiched between dielectric layers for electrical isolation.
4. Heat Dissipation: They are effective at spreading heat away from heat-generating components and distributing it across the board, preventing localized overheating.
Differences:
1. Core Material: The most significant difference is the core material. Copper Core PCBs have a core made primarily of copper, whereas Aluminum Core PCBs have a core made primarily of aluminum. Copper has higher thermal conductivity than aluminum, which makes Copper Core PCBs more efficient at heat dissipation.
2. Thermal Conductivity: Copper has a significantly higher thermal conductivity (around 398 W/m·K) compared to aluminum (around 205 W/m·K). This means that Copper Core PCBs can handle higher heat loads and provide better thermal performance.
3. Weight: Aluminum Core PCBs are generally lighter than Copper Core PCBs, which can be advantageous in applications where weight is a concern.
4. Cost: Copper Core PCBs tend to be more expensive than Aluminum Core PCBs due to the higher cost of copper and the manufacturing challenges associated with working with copper.
5. Thermal Expansion: Aluminum has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) compared to copper. This can lead to differences in thermal expansion between the core material and the components, which designers must account for in their designs.
6. Electrical Conductivity: Copper is an excellent electrical conductor, so Copper Core PCBs may require additional insulation and design considerations to prevent electrical shorts between traces or components on different layers. Aluminum Core PCBs are non-conductive, which simplifies electrical isolation.
In summary, both Copper Core PCBs and Aluminum Core PCBs serve the purpose of efficient heat dissipation, but they differ significantly in terms of their core materials, thermal conductivity, weight, cost, and electrical properties. The choice between them depends on the specific requirements of the application and the balance between cost and thermal performance. Copper Core PCBs are typically preferred for applications with very high heat dissipation requirements, while Aluminum Core PCBs are suitable for applications where cost and weight are more critical considerations.
How to choose the correct copper core PCB supplier?
Choosing the right Copper Core PCB supplier is crucial, especially when you need PCBs with excellent thermal conductivity for applications that generate significant heat. Here are steps to help you select the correct Copper Core PCB supplier:
- Define Your Requirements:
- Clearly specify your Copper Core PCB requirements, including size, thickness, copper core material type (e.g., copper, aluminum), thermal conductivity, dielectric material, and any specific technical requirements like impedance control or thermal management needs.
- Experience and Expertise:
- Look for PCB suppliers with extensive experience in manufacturing Copper Core PCBs. Check if they have a proven track record in producing high-quality boards for applications similar to yours.
- Inquire about their expertise in thermal management and heat dissipation solutions.
- Quality Assurance and Certifications:
- Ensure the supplier adheres to quality control standards such as ISO 9001 and ISO 14001. Look for certifications relevant to your industry, such as automotive or aerospace standards.
- Ask about their quality assurance processes and their commitment to delivering defect-free PCBs.
- Material Selection:
- Verify that the supplier offers a range of core material options with varying thermal conductivity properties, and choose the one that best suits your needs.
- Ensure they source high-quality copper or aluminum core materials and that they can provide documentation on material properties.
- Technical Support:
- Evaluate the supplier’s willingness and ability to offer technical support during the design phase. They should be able to assist with thermal design considerations and suggest improvements to optimize heat dissipation.
- Samples and Prototyping:
- Before committing to a large production order, request samples or prototypes to assess the quality and performance of the Copper Core PCBs they produce.
- Lead Times and Production Capacity:
- Determine the supplier’s lead times for production and delivery. Make sure they can accommodate your project’s timeline.
- Check if they have the production capacity to handle your order size and any potential volume fluctuations.
- Cost and Pricing:
- Obtain detailed quotes from multiple Copper Core PCB suppliers to compare pricing. Be cautious of significantly lower prices, as they may indicate subpar quality.
- Consider the overall cost, including shipping and any additional fees.
- Communication and Responsiveness:
- Gauge the supplier’s communication skills and responsiveness. Effective communication is vital for addressing issues, changes, and clarifications in a timely manner.
- Geographical Considerations:
- Assess the supplier’s location and proximity to your facility. This can impact shipping costs, lead times, and communication ease.
- Environmental Practices:
- Inquire about the supplier’s environmental practices and commitment to sustainability. Sustainability considerations are increasingly important in manufacturing.
- Customer References:
- Ask for customer references and contact these references to gather feedback on their experiences with the Copper Core PCB supplier.
- Contracts and Agreements:
- Carefully review all contracts and agreements to ensure they cover important aspects such as quality standards, material sourcing, intellectual property protection, and dispute resolution.
- Visit the Facility:
- If possible, visit the Copper Core PCB supplier’s manufacturing facility to inspect their equipment, quality control processes, and overall capabilities.
Choosing the correct Copper Core PCB supplier requires thorough research and due diligence. Quality, reliability, and the supplier’s expertise in thermal management are of utmost importance to ensure your electronic devices perform optimally while effectively dissipating heat.
Welcome to custom Copper Prototype Board directly from PCB Manufacturer China Shenzhen at low cost.
Main Equipments