Advantages of rigid flex PCB used in automobile.
In order to successfully solve the problems mentioned in the first paragraph, flex rigid PCB has been used to reduce the number of connectors and solder joints for more than 15 years. Due to the application of flex rigid PCB in automobile system, the following advantages can be adopted.
Significantly improve product quality and reliability
When flex rigid PCB is applied to automobile, connector and welded joint can be reduced, which can reduce the potential risk of electrical failure. The performance and reliability of automotive electronic control system will be proportional to the reduction of connectors and welded joints.
Lower costs due to reduced manufacturing steps
With the application of flex rigid PCB, the welding of ribbon cable and assembly connector will be cut, so as to reduce the cost. After all, the implementation of all manufacturing processes is expensive.
Flex rigid pcb for automobile is composed of two or more rigid materials and one or more flexible materials, and the rigid parts are connected with each other through the application of flexible materials. Each rigid flexible combination circuit can be precisely packaged in a smaller package, which can eliminate a lot of management and maintenance.
Flex rigid circuit designers are only responsible for rigid PCB layout. For flexible parts, they only need to guide the connection, and can be freely fixed, suspended or driven, which greatly simplifies the design and PCB assembly.
So far, there are two types of flexible and rigid PCBs:
a. Semi flexible PCB. The flexible part of semi flexible PCB is made of thin FR-4 material, which is especially suitable for assembly with only a few kinds of flexibility. In addition, semi flexible PCB leads to low cost.
b. Multilayer flexible PCB. Multilayer flexible PCB is made of polyimide (PI) material, which can meet the requirements of dynamic flexibility. Because PI layer can be extended to the internal rigid part of rigid flexible PCB, multilayer flexible PCB is more suitable for applications that need gradual dynamic flexibility.
Multilayer flexible PCB
The flexible part of rigid flexible PCB is made of flexible PI copper foil, which belongs to multilayer flexible PCB. Multilayer flexible PCB is a traditional rigid flexible PCB, which has been used for more than 30 years. The multilayer flexible PCB has a hybrid structure composed of a rigid substrate material and a flexible substrate material, and the interconnection between the electrical conductors is realized through an electroplating through hole which passes through the rigid and flexible materials. Figure 1 below shows the structure of the two-layer flexible circuit board.
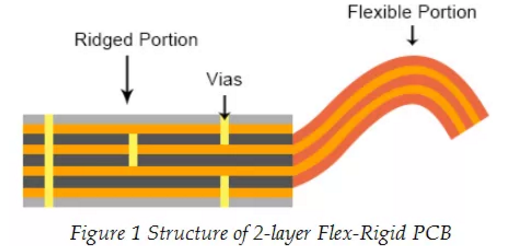
According to figure 1, it can be concluded that the flexible substrate material depends on the common PI copper foil material, which is not only laid on the flexible part, but also covers all the rigid parts. However, it is equivalent to lay some PI copper foil in the selective section. Once the flexible PI copper foil is used in the selective part, the manufacturing complexity will increase, and this method is rarely used.
When it comes to multilayer flexible PCB, due to the relatively high CTE (coefficient of thermal expansion) along the z-axis bonding direction, the adhesive may cause mechanical damage to the plated via during pressure test or thermal shock test. Therefore, when the Automotive PCB requires higher thermal reliability, it is necessary to avoid the use of flexible substrate materials and the covering layer covered in the rigid part, because electroplated vias are usually used in the rigid part.
In addition, because FR4 prepreg is also a kind of substrate with high CTE, the reliability of common FR4 binder and non flowing prepreg must be considered. The Tg of ordinary FR4 non flowing prepreg is 105 ° C, which is about 30 ° C lower than that of traditional FR4 prepreg.
In addition to FR4 material used as rigid substrate, almost any type of rigid material is suitable for multi flexible PCB, including high Tg material, halogen-free material and even high frequency material.
Most flexible materials are used for rigid and flexible PCB, using PI with adhesive or PI without adhesive, the effect is better. However, pen and PET materials can also be used for simple and asymmetric flexible rigid circuit board structures. LCP (liquid crystal polymer) can be regarded as the best flexible material without adhesive, which has high reliability design and high speed signal transmission design. It is recommended that they be baked before application to eliminate humidity due to high humidity absorption of PI. However, multi flexible PCB using LCP as substrate material does not need baking.
In terms of flexible rigid pcb, multilayer flexible circuit can provide some flexible layers, which can be used at the same time. Because the complex interconnection of the circuit is integrated design, it can be manufactured repeatedly, which is more advantageous than cable and wire connection. Therefore, the coaxial cable can be used to control the impedance of signal transmission.
Semi flexible PCB
Semi flexible PCB can not achieve continuous flexibility. In fact, in many applications, the flexible part of rigid flexible PCB only has some flexibility, such as during assembly, rework and maintenance. Therefore, expensive flexible materials such as PI are not necessary for this application and the use of flexible materials is sufficient. In addition, it can reduce the cost. Semi flexible PCB can use traditional substrate materials for multi-layer lamination, so as to avoid different materials laminating together, and minimize the internal thermal stress. In order to obtain flexible materials, the best way is to make the traditional FR4 substrate material bending enough. Of course, another method is to selectively reduce the thickness of the flexible part.
It adheres to the same manufacturing technology as traditional double-sided PCB and semi flexible PCB. The thinning of the flexible part can be accomplished by milling. In addition, semi flexible PCB is manufactured by adhering to the similar manufacturing technology of traditional PCB, in addition to increasing flexible PCB manufacturing.