As electronic technology continues to advance, printed circuit boards (PCBs) play a crucial role in various electronic devices. However, in achieving high performance, reliability, and longevity, the surface treatment of PCBs is essential. This article will focus on PCB brown oxide, an important surface treatment step that helps improve the performance and solderability of PCBs.
PCB brown oxide is a surface treatment process typically achieved through oxidation. In PCB manufacturing, copper is one of the most commonly used conductive materials due to its excellent conductivity. However, copper surfaces are susceptible to oxidation and corrosion, which can reduce the performance and reliability of PCBs. To address this issue, PCB manufacturers employ the brown oxide process.
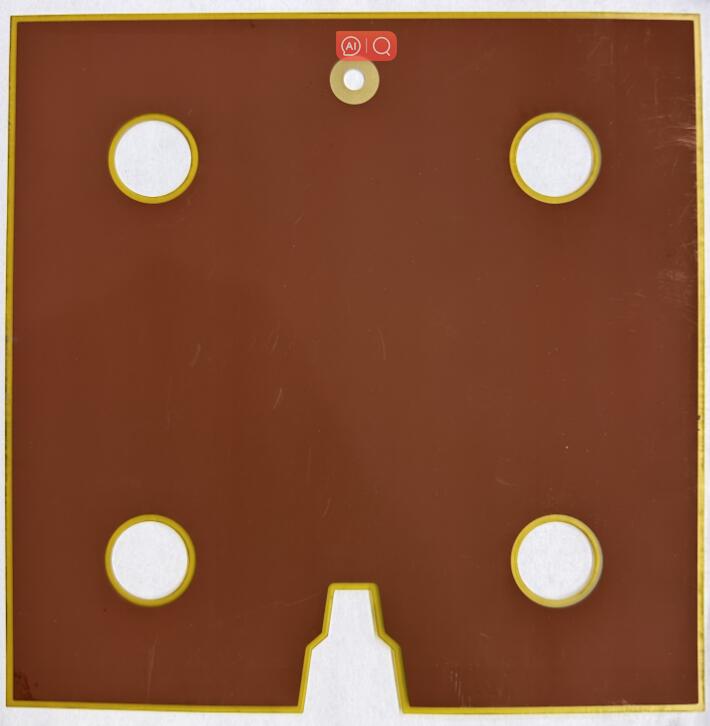
The fundamental principle of PCB brown oxide is to form a layer of copper oxide by exposing the copper surface to oxygen or other oxidizing agents. This oxide layer typically appears brown, hence the name “PCB brown oxide.” This oxide layer serves several crucial purposes:
PCB brown oxide is typically carried out early in the manufacturing process. Here are the general steps involved in PCB brown oxide:
PCB brown oxide is a critical step in the PCB manufacturing process, contributing to the improved performance, reliability, and solderability of PCBs. By forming a brown oxide layer, the copper surface of the PCB is effectively protected and becomes more amenable to reliable connections with electronic components. This essential surface treatment step ensures that PCBs perform admirably across various applications, driving the advancement of modern electronic technology.
“Aminobenzotriazole” and “Aminobenzotriazole” are actually the same chemical compound, commonly referred to as “Aminobenzotriazole” or “Benzotriazole.” This compound is often used in metal surface treatment, especially in electronics manufacturing and printed circuit board (PCB) production, as a copper-affinitive, surface-active additive to improve the adhesion and corrosion resistance of copper surfaces. Different sources or manufacturers may use different naming conventions, but they typically refer to the same compound.