Thick/Heavy copper PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) are specialized circuit boards designed to handle high current and provide enhanced durability for various electronic applications. They are also known as thick copper PCBs, and they have thicker copper traces or layers compared to standard PCBs. Here are some key points to understand about heavy copper PCBs:
In summary, heavy copper PCBs are specialized circuit boards designed to handle high current and provide enhanced durability. They are commonly used in applications where power and reliability are critical, making them a valuable choice in various industries. However, their increased cost and design complexity should be taken into account when selecting them for a particular project.
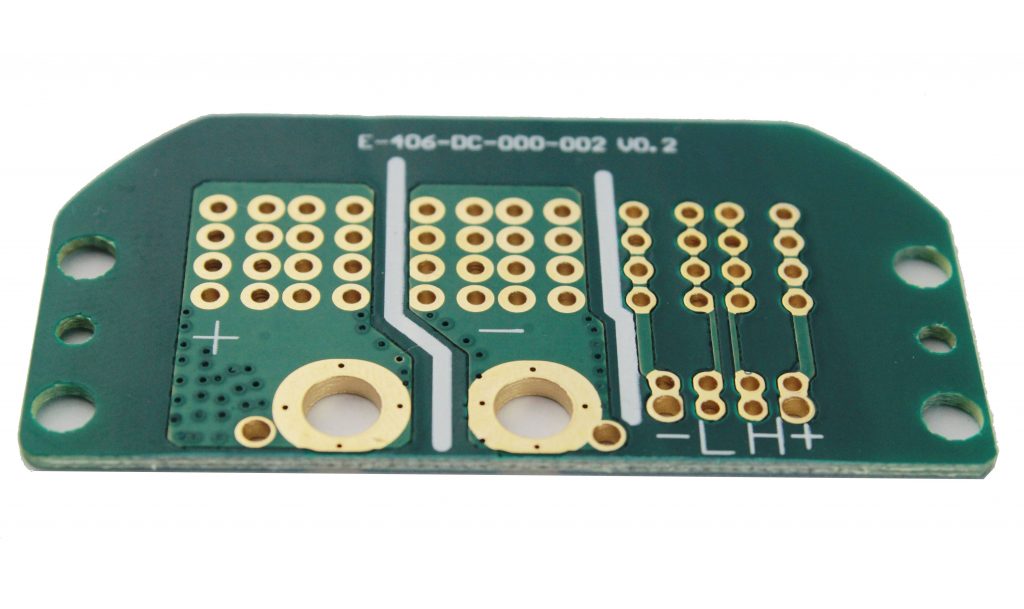

The design and production of heavy copper PCBs come with some additional challenges and complexities compared to regular PCBs. These challenges typically include the following aspects:
So designing and manufacturing heavy copper PCBs require additional considerations in terms of processes and materials to ensure they meet high-current and durability requirements. These challenges should be taken into account early in the project to successfully produce high-quality heavy copper PCBs.
Choosing the right heavy copper PCB supplier is a crucial step in ensuring the success of your project. Here are some considerations to help you select the appropriate heavy copper PCB supplier:
Ultimately, choosing the right heavy copper PCB supplier requires a comprehensive assessment of multiple factors to ensure they can meet your project needs and provide high-quality products and services. Take your time to research and compare different suppliers to make an informed decision.
Our thickest copper PCB can make 12 ounces. However, considering the side eclipse factor, copper thickness of more than 3 ounces should pay special attention to the line width of the inner layer.
Inner 3 oz copper PCB: line width 6/7 mil outer 3 ounces: line width 8/12 mil
Inner layer 4 oz copper PCB: line width line spacing 8/11 mil outer layer 3 ounces: line width line spacing 9/15 mil
Inner 5 oz copper PCB: line width 10/16 mil outer 3 ounces: line width 11/16 mil
Inner 6 oz copper PCB: line width line spacing 12/18 mil outer layer 3 ounces: line width line spacing 14/18 mil

